- Latest news▼
-
15:11, April 24 Zombie deer disease possibly linked to hunters’ deaths

-
12:27, April 23 Appetite: Scientists found out the secret to the appeal of large portions of fast food

-
10:33, April 23 Scientists test new approach to fighting viruses

-
08:38, April 23 Ketamine may help with postpartum depression

-
22:12, April 22 Unhealthy amount of sugar found in baby food products of a well-known brand

-
19:41, April 22 Air pollution puts health of more than 1.6 billion workers globally at risk

-
17:25, April 22 Scientists found baked goods and lack of sleep to be more dangerous than alcohol

-
16:02, April 22 342 cases of measles recorded in Armenia so far in 2024
-
15:29, April 22 BrainStimulation: electrical brain stimulation alleviates anxiety and depression in the elderly

-
08:27, April 22 Cognitively stimulating jobs in midlife could lower dementia risk in old age, study finds

-
20:37, April 21 Environmental Health Perspectives: Microplastics ingested with food and water can spread from the gut to the brain

-
22:41, April 20 Scientists develop new method to safely stimulate immune cells to fight cancer
-
20:46, April 20 Blood test can determine who is at risk of developing multiple sclerosis - scientists

-
18:36, April 20 Next pandemic likely to be triggered by flu - scientists

-
12:16, April 19 Scientists grow human mini-lungs in lab

All materials
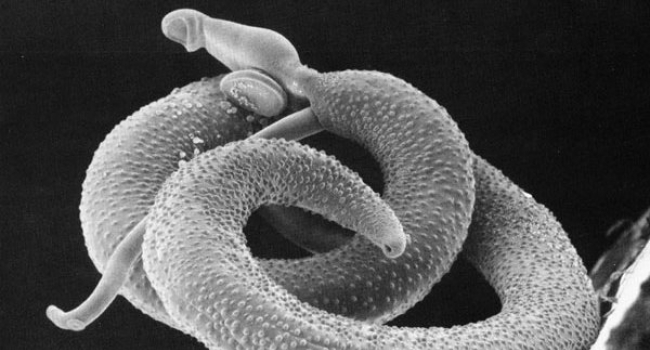
Schistosomiasis is associated with incident HIV transmission and death in Zambia
Background
We examined relationships between schistosome infection, HIV transmission or acquisition, and all-cause death.
Methods
We retrospectively tested baseline sera from a heterosexual HIV-discordant couple cohort in Lusaka, Zambia with follow-up from 1994–2012 in a nested case-control design. Schistosome-specific antibody levels were measured by ELISA. Associations between baseline antibody response to schistosome antigens and incident HIV transmission, acquisition, and all-cause death stratified by gender and HIV status were assessed. In a subset of HIV- women and HIV+ men, we performed immunoblots to evaluate associations between Schistosoma haematobium or Schistosoma mansoni infection history and HIV incidence.
Results
Of 2,145 individuals, 59% had positive baseline schistosome-specific antibody responses. In HIV+ women and men, baseline schistosome-specific antibodies were associated with HIV transmission to partners (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR] = 1.8, p<0.005 and aHR = 1.4, p<0.05, respectively) and death in HIV+ women (aHR = 2.2, p<0.001). In 250 HIV- women, presence of S. haematobium-specific antibodies was associated with increased risk of HIV acquisition (aHR = 1.4, p<0.05).
Conclusion
Schistosome infections were associated with increased transmission of HIV from both sexes, acquisition of HIV in women, and increased progression to death in HIV+ women. Establishing effective prevention and treatment strategies for schistosomiasis, including in urban adults, may reduce HIV incidence and death in HIV+ persons living in endemic areas.
Author summary
This study explored the association between schistosome infections (a disease caused by parasitic flatworms, also known as ‘snail fever’, which is very common throughout sub-Saharan Africa) and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). We found in Lusaka, the capital of Zambia, that schistosome infections were associated with transmission of HIV from adult men and women, and schistosome infections were also associated with increased HIV acquisition in adult women. We additionally found that schistosome infections were associated with death in HIV+ adult women. Since treatment of schistosome infections with praziquantel is inexpensive, effective, and safe, schistosomiasis prevention and treatment strategies may be a cost-effective way to reduce not only the symptoms associated with the infection, but also new cases of HIV and death among HIV+ persons. Though often viewed as an infection of predominantly rural areas and children, this study highlights that schistosomiasis prevention and treatment efforts are also needed in urban areas and among adults.
Full article: PLoS Neglected Tropical Diseases
Follow NEWS.am Medicine on Facebook and Twitter
- Video
- Event calendar
- Archive
- Most read
month
week
day
- JAMA Oncology: Urine test can help rule out high-grade prostate cancer with almost 100% accuracy, study shows 1240
- Daily Mail: Elderly woman in China gets infected with brain-eating amoeba 1186
- Obesity: exercising before breakfast helps you lose weight faster 1168
- The Conversation: childhood trauma can cause pathological hoarding 1164
- Scientists grow human mini-lungs in lab 1131
- Next pandemic likely to be triggered by flu - scientists 835
- Scientists found baked goods and lack of sleep to be more dangerous than alcohol 756
- 342 cases of measles recorded in Armenia so far in 2024 715
- Blood test can determine who is at risk of developing multiple sclerosis - scientists 697
- Scientists develop new method to safely stimulate immune cells to fight cancer 693
- Cognitively stimulating jobs in midlife could lower dementia risk in old age, study finds 675
- BrainStimulation: electrical brain stimulation alleviates anxiety and depression in the elderly 627
- Air pollution puts health of more than 1.6 billion workers globally at risk 492
- Unhealthy amount of sugar found in baby food products of a well-known brand 484
- Ketamine may help with postpartum depression 469
- Find us on Facebook
- Poll