- Latest news▼
-
15:32, April 26 ESCMID: New method of purifying the air with ultraviolet light could protect world from new pandemic

-
08:43, April 26 Enzymes that convert different blood groups into first group are discovered

-
19:41, April 25 Children’s Hospital Los Angeles and International Center of Professional Development Allergy/Immunology Conference

-
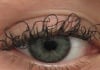
17:31, April 25 JAMA: patient grew long, curly eyelashes because of chemotherapy
-
11:08, April 25 Mpox epidemic declared in Republic of the Congo

-
08:31, April 25 OU: quitting smoking 4 times more likely to cure laryngeal cancer

-
01:20, April 25 Paralyzed man in China writes hieroglyphs using neural implants placed in his brain

-
15:11, April 24 Zombie deer disease possibly linked to hunters’ deaths

-
12:27, April 23 Appetite: Scientists found out the secret to the appeal of large portions of fast food

-
10:33, April 23 Scientists test new approach to fighting viruses

-
08:38, April 23 Ketamine may help with postpartum depression

-
22:12, April 22 Unhealthy amount of sugar found in baby food products of a well-known brand

-
19:41, April 22 Air pollution puts health of more than 1.6 billion workers globally at risk

-
17:25, April 22 Scientists found baked goods and lack of sleep to be more dangerous than alcohol

-
16:02, April 22 342 cases of measles recorded in Armenia so far in 2024
All materials
UofL: excess sun may provoke plaque buildup in arteries

American scientists have found out that staying in the air during a heat wave can increase inflammatory processes and increase the risks of cardiovascular diseases.
According to the University of Louisville (UofL) website, 624 adult volunteers participated in the study organized by University of Louisville staff. From May 2018 to September 2019, blood samples were taken from them in the summer to record the number of inflammatory markers. The average temperature on the days of the tests was 24.5 degrees Celsius.
The scientists studied the levels of basic compounds that the immune system generates when it detects damage - T and B cells. The levels of cytokines (signaling molecules that can trigger inflammation in the body) were also analyzed.
Inflammatory markers were then compared to levels of heat, UV light, wind, and humidity. These factors were combined into a Universal Thermal Climate Index (UTCI).
It turned out that each five-point increase in UTCI caused an increase in the number of natural killer T-cells in the participants' blood. Killer cells are cells of innate immunity that destroy pathogens. Their activation is also an indicator of triggering inflammation in the body.
Inflammation remains the body's natural defense algorithm against infection. However, a prolonged inflammatory response plays a key role in the appearance of plaques in the arteries. They block the lumen of the vessels, making it difficult to supply normal blood to organs and tissues. Which can lead to coronary heart disease and heart attack.
We have also recently been reminded of what foods should be mandatory on the menu to protect the heart and blood vessels from pathologies.
Follow NEWS.am Medicine on Facebook and Twitter
- Video
- Event calendar
- Children’s Hospital Los Angeles and International Center of Professional Development Allergy/Immunology Conference
- First Armenian-German Conference entitled “Heart Failure Spring School”
- Allogeneic bone marrow transplant in case of hematological malignancy performed in Armenia for first time
All materials
- Archive
- Most read
month
week
day
- Scientists found baked goods and lack of sleep to be more dangerous than alcohol 1047
- Next pandemic likely to be triggered by flu - scientists 1029
- 342 cases of measles recorded in Armenia so far in 2024 970
- Unhealthy amount of sugar found in baby food products of a well-known brand 874
- Air pollution puts health of more than 1.6 billion workers globally at risk 869
- Ketamine may help with postpartum depression 865
- Appetite: Scientists found out the secret to the appeal of large portions of fast food 856
- Scientists test new approach to fighting viruses 837
- Scientists develop new method to safely stimulate immune cells to fight cancer 832
- Cognitively stimulating jobs in midlife could lower dementia risk in old age, study finds 828
- Blood test can determine who is at risk of developing multiple sclerosis - scientists 826
- Zombie deer disease possibly linked to hunters’ deaths 790
- BrainStimulation: electrical brain stimulation alleviates anxiety and depression in the elderly 759
- Mpox epidemic declared in Republic of the Congo 597
- Paralyzed man in China writes hieroglyphs using neural implants placed in his brain 569
- Find us on Facebook
- Poll