- Latest news▼
-
15:32, April 26 ESCMID: New method of purifying the air with ultraviolet light could protect world from new pandemic

-
08:43, April 26 Enzymes that convert different blood groups into first group are discovered

-
19:41, April 25 Children’s Hospital Los Angeles and International Center of Professional Development Allergy/Immunology Conference

-
17:31, April 25 JAMA: patient grew long, curly eyelashes because of chemotherapy
-
11:08, April 25 Mpox epidemic declared in Republic of the Congo

-
08:31, April 25 OU: quitting smoking 4 times more likely to cure laryngeal cancer

-
01:20, April 25 Paralyzed man in China writes hieroglyphs using neural implants placed in his brain

-
15:11, April 24 Zombie deer disease possibly linked to hunters’ deaths

-
12:27, April 23 Appetite: Scientists found out the secret to the appeal of large portions of fast food

-
10:33, April 23 Scientists test new approach to fighting viruses

-
08:38, April 23 Ketamine may help with postpartum depression

-
22:12, April 22 Unhealthy amount of sugar found in baby food products of a well-known brand

-
19:41, April 22 Air pollution puts health of more than 1.6 billion workers globally at risk

-
17:25, April 22 Scientists found baked goods and lack of sleep to be more dangerous than alcohol

-
16:02, April 22 342 cases of measles recorded in Armenia so far in 2024
All materials
What obesity does to your brain
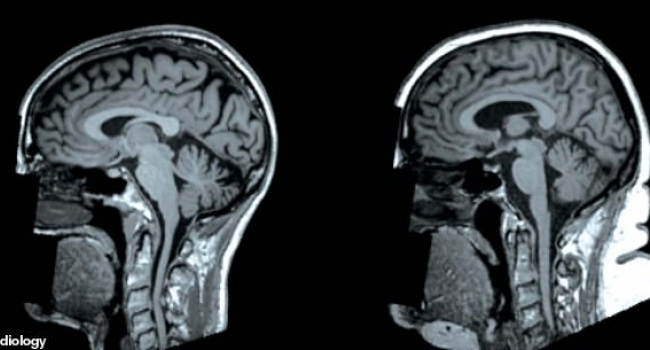
Fascinating scans reveal obesity affects the structure of a person's brain.
A study that collected MRI scans of thousands of people of different sizes found those carrying dangerous amounts of weight have 'smaller volumes of important structures of the brain'.
Less grey matter suggests a loss of nerve cells, while changes to white matter may affect how electrical signals are transmitted within the vital organ.
And since grey matter plays a role in our 'reward centre', these changes may make it difficult for obese people to control their weight, researchers claim.
Obesity is thought to lead to inflammation that damages brain tissue, however, this is unclear.
The research was carried out by Leiden University Medical Center in the Netherlands and led by Dr Ilona Dekkers, a radiologist.
'We found that having higher levels of fat distributed over the body is associated with smaller volumes of important structures of the brain, including grey matter structures that are located in the center of the brain,' Dr Dekkers said.
'Interestingly, we observed that these associations are different for men and women, suggesting that gender is an important modifier of the link between fat percentage and the size of specific brain structures.'
Obesity is a global concern, with 26 per cent of adults carrying dangerous amounts of weight in the UK in 2016, NHS statistics show.
And in the US, 39.8 per cent of adults were obese in 2015-to-2016, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
To determine how obesity affects the brain, the researchers analysed the MRI scans of 12,087 participants of the UK Biobank study.
Since it started in 2006, Biobank has gathered the genetic information of half-a-million people, and aims to uncover how DNA and lifestyle factors influence our risk of disease.
The scans were carried out with state-of-the-art technology that distinguishes between grey and white matter.
'MRI has shown to be an irreplaceable tool for understanding the link between neuroanatomical differences of the brain and behavior,' Dr Dekkers said.
In simple terms, grey matter contains the bulk of our nerve cells, while white matter is made up of long filaments that transmit electrical signals between neurones.
Results - published in the journal Radiology - revealed the participants' weight led to clear differences in the make-up of their brains.
'Our study shows that very large data collection of MRI data can lead to improved insight into exactly which brain structures are involved in all sorts of health outcomes, such as obesity,' Dr Dekkers said.
These outcomes were also sex related. The men with a higher total body fat percentage had a lower grey matter volume. They also had impaired structures that relate to 'reward circuitry' and movement.
Reward circuitry refers to a group of structures that are activated by a reinforcing stimulus, such as addictive drugs.
The results further revealed the larger female participants had reduced activity in their globus pallidus, which is a structure that regulates voluntary movement.
For both men and women, a higher total body fat percentage increased the likelihood of microscopic changes to their brain's white matter.
But the study only looked at body fat percentage and did not distinguish between different types of fat, the researchers stress.
Of particular interest is the visceral white fat found around our internal abdominal organs, which increases our risk of heart disease and type 2 diabetes.
Study author Dr Hildo Lamb, professor of radiology, added: 'For future research, it would be of great interest whether differences in body fat distribution are related to differences in brain morphological structure.
'Visceral fat is a known risk factor for metabolic disease and is linked to systemic low-grade inflammation.'
Source: The Daily Mail
Follow NEWS.am Medicine on Facebook and Twitter
- Video
- Event calendar
- Children’s Hospital Los Angeles and International Center of Professional Development Allergy/Immunology Conference
- First Armenian-German Conference entitled “Heart Failure Spring School”
- Allogeneic bone marrow transplant in case of hematological malignancy performed in Armenia for first time
All materials
- Archive
- Most read
month
week
day
- Scientists found baked goods and lack of sleep to be more dangerous than alcohol 1046
- Next pandemic likely to be triggered by flu - scientists 1026
- 342 cases of measles recorded in Armenia so far in 2024 969
- Unhealthy amount of sugar found in baby food products of a well-known brand 863
- Air pollution puts health of more than 1.6 billion workers globally at risk 858
- Ketamine may help with postpartum depression 854
- Appetite: Scientists found out the secret to the appeal of large portions of fast food 845
- Scientists develop new method to safely stimulate immune cells to fight cancer 830
- Cognitively stimulating jobs in midlife could lower dementia risk in old age, study finds 827
- Scientists test new approach to fighting viruses 826
- Blood test can determine who is at risk of developing multiple sclerosis - scientists 825
- Zombie deer disease possibly linked to hunters’ deaths 777
- BrainStimulation: electrical brain stimulation alleviates anxiety and depression in the elderly 757
- Mpox epidemic declared in Republic of the Congo 586
- Paralyzed man in China writes hieroglyphs using neural implants placed in his brain 556
- Find us on Facebook
- Poll