- Latest news▼
-
15:32, April 26 ESCMID: New method of purifying the air with ultraviolet light could protect world from new pandemic

-
08:43, April 26 Enzymes that convert different blood groups into first group are discovered

-
19:41, April 25 Children’s Hospital Los Angeles and International Center of Professional Development Allergy/Immunology Conference

-
17:31, April 25 JAMA: patient grew long, curly eyelashes because of chemotherapy
-
11:08, April 25 Mpox epidemic declared in Republic of the Congo

-
08:31, April 25 OU: quitting smoking 4 times more likely to cure laryngeal cancer

-
01:20, April 25 Paralyzed man in China writes hieroglyphs using neural implants placed in his brain

-
15:11, April 24 Zombie deer disease possibly linked to hunters’ deaths

-
12:27, April 23 Appetite: Scientists found out the secret to the appeal of large portions of fast food

-
10:33, April 23 Scientists test new approach to fighting viruses

-
08:38, April 23 Ketamine may help with postpartum depression

-
22:12, April 22 Unhealthy amount of sugar found in baby food products of a well-known brand

-
19:41, April 22 Air pollution puts health of more than 1.6 billion workers globally at risk

-
17:25, April 22 Scientists found baked goods and lack of sleep to be more dangerous than alcohol

-
16:02, April 22 342 cases of measles recorded in Armenia so far in 2024
All materials
Specialised MRI can predict who will develop treatment-resistant schizophrenia - study
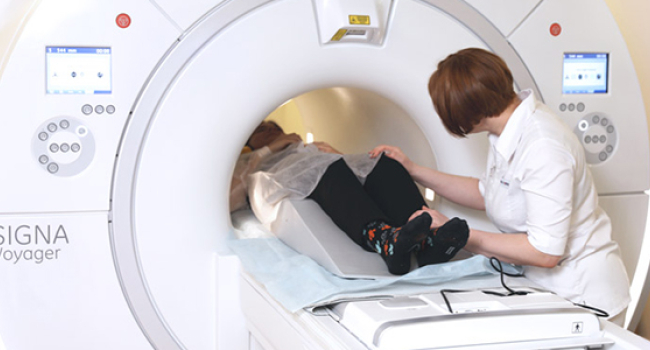
A specialised brain scan can accurately predict whether a patient with psychosis will develop treatment-resistant schizophrenia, Dutch researchers have found.
Neuromelanin-sensitive MRI scans, or NM-MRI for short, target a brain pigment called neuromelanin. This pigment can provide visual evidence of healthy dopamine function.
Dopamine is a hormone that is part of the reward system in the brain. Too much dopamine can lead to aggression and poor impulse control associated with psychosis.
The study authors, led by Marieke van der Plim, a postdoctoral researcher at the University of Amsterdam, believe that NM -MRI could be a game changer.
"There is an urgent need for markers to identify unresponsive schizophrenia patients at an early stage and to facilitate timely initiation of clozapine, the only antipsychotic with proven efficacy in unresponsive patients," they write in The American Journal of Psychiatry.
Unlike patients who respond to treatment, patients with treatment-resistant schizophrenia do not show an increase in dopamine function. According to the researchers, this suggests that neuromelanin levels - a control measure of dopamine function - may be an early marker of treatment resistance.
The study included 62 patients aged 18 to 35 who had a first psychotic episode. All of them were diagnosed with schizophrenia. These patients were compared with a control group of 20 healthy volunteers.
All patients underwent a clinical interview, IQ test and NM -MRI scan, while the patients with psychosis received antipsychotic treatment.
After six months, response to treatment was assessed. Those who continued to have moderate or severe symptoms in one of five domains, including delusions, hallucinations, postures, and unusual thoughts, after two courses of antipsychotic medication were considered unresponsive to treatment.
Patients who did not respond to a single antipsychotic or experienced serious side effects or were switched to clozapine during follow-up were also considered non-responders.
Of the 62 patients, 47 were considered to have responded.
At baseline NM -MRI, 15 of the non-responders appeared to have significantly reduced signal in a region of the brain called the substantia nigra. It is rich in dopamine neurons and regulates emotions and reward-related behaviour, among other things.
Based on the neuromelanin data, the researchers were able to predict with 68 per cent accuracy which patients would respond to the treatment.
In 28 patients who responded to treatment and nine patients who did not respond to treatment who underwent repeat scans, the NM -MRI signal did not change for six months.
Follow NEWS.am Medicine on Facebook and Twitter
- Video
- Event calendar
- Children’s Hospital Los Angeles and International Center of Professional Development Allergy/Immunology Conference
- First Armenian-German Conference entitled “Heart Failure Spring School”
- Allogeneic bone marrow transplant in case of hematological malignancy performed in Armenia for first time
All materials
- Archive
- Most read
month
week
day
- Scientists found baked goods and lack of sleep to be more dangerous than alcohol 1059
- Next pandemic likely to be triggered by flu - scientists 1047
- 342 cases of measles recorded in Armenia so far in 2024 978
- Unhealthy amount of sugar found in baby food products of a well-known brand 937
- Air pollution puts health of more than 1.6 billion workers globally at risk 926
- Ketamine may help with postpartum depression 917
- Appetite: Scientists found out the secret to the appeal of large portions of fast food 912
- Scientists test new approach to fighting viruses 892
- Zombie deer disease possibly linked to hunters’ deaths 858
- Scientists develop new method to safely stimulate immune cells to fight cancer 842
- Cognitively stimulating jobs in midlife could lower dementia risk in old age, study finds 837
- Blood test can determine who is at risk of developing multiple sclerosis - scientists 835
- BrainStimulation: electrical brain stimulation alleviates anxiety and depression in the elderly 770
- Mpox epidemic declared in Republic of the Congo 654
- Paralyzed man in China writes hieroglyphs using neural implants placed in his brain 633
- Find us on Facebook
- Poll