- Latest news▼
-
14:07, July 26 Specialist: We have drop in hepatitis cases in Armenia, but rare cases of acute Hepatitis B and C are recorded

-
13:29, July 26 Nature Chemical Biology: Scientists develop new antibiotic against super bacteria

-
11:36, July 26 New deadly disease reported in the world

-
10:17, July 25 Researchers name oats that help lose weight almost like Ozempic

-
08:34, July 25 Using 'mini-lungs,' scientists find that more types of lung cells can be infected by SARS-CoV-2 than previously thought
-
14:31, July 24 Cyprus has seen increase in coronavirus cases

-
12:16, July 24 Developmental Medicine & Child Neurology: Botox injections could make walking easier in children with cerebral palsy
-
12:20, July 23 There is high risk of dengue fever spread in Iran, WHO announces

-
10:15, July 23 AIDS can end by 2030 if world leaders make the right decisions now, UNAIDS says

-
19:42, July 22 JAMA: A mother's healthy diet reduces the risk of having a child with autism by 22%

-
15:37, July 22 CellMet: interval fasting and a healthy diet improved brain function of the elderly

-
11:26, July 22 Nutrition: coffee reduces the risk of polycystic ovary syndrome

-
15:11, July 19 RFSN: Vitamin C deficiency in the body correlates with weight gain

-
08:38, July 19 Western diets increase the risk of inflammatory bowel disease and colorectal cancer - a review
-
20:45, July 18 Researchers have identified a signaling pathway that transforms epithelial cells into aggressive tumor cells
All materials
APL Materials: Antibacterial hydrogel is developed for treatment of non-healing wounds
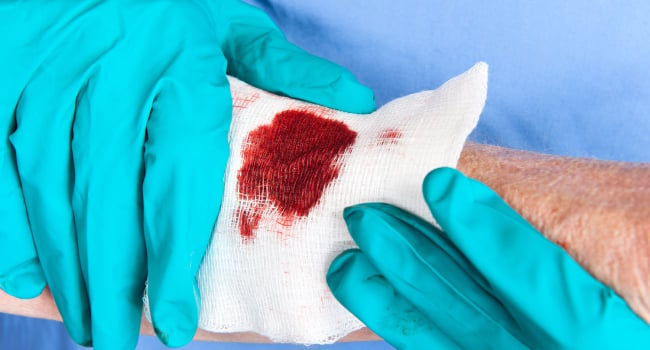
Researchers from Jilin University (China) have created the first antibacterial hydrogel of its kind, which is intended for the treatment of non-healing wounds.
The respective research was published in the journal APL Materials.
Hydrogels are in great demand in medicine to help with skin diseases and in tissue engineering. But they are difficult to make, these materials are unstable to external influences, such as contact with clothes, sheets or bandages. By their nature, these substances cannot fight against bacterial infections, and therefore they need to be combined with antibiotics, which often slow down cell growth and prevent healing.
Specialists, however, have solved these problems by adding polylysine amino acid and blood plasma rich in platelets to the usual Gel-MA hydrogel. Polylysine acts as a natural antibiotic and suppresses microorganisms, and blood plasma accelerates tissue healing. Also, these additions made the material more stable.
According to the researchers, the Gel-MA, polylysine, and plasma composition turns into a gel in 30 seconds under a UV lamp, while standard hydrogels need to be cooled every now and then to maintain their flexibility.
The researchers expect that the material they created will help patients with diabetes and some other diseases whose skin wounds do not heal.
Follow NEWS.am Medicine on Facebook and Twitter
- Most read
month
week
day
- CellMet: interval fasting and a healthy diet improved brain function of the elderly 1224
- Nutrition: coffee reduces the risk of polycystic ovary syndrome 1157
- JAMA: A mother's healthy diet reduces the risk of having a child with autism by 22% 1109
- There is high risk of dengue fever spread in Iran, WHO announces 1085
- AIDS can end by 2030 if world leaders make the right decisions now, UNAIDS says 958
- Developmental Medicine & Child Neurology: Botox injections could make walking easier in children with cerebral palsy 793
- Cyprus has seen increase in coronavirus cases 707
- Researchers name oats that help lose weight almost like Ozempic 597
- Using 'mini-lungs,' scientists find that more types of lung cells can be infected by SARS-CoV-2 than previously thought 545
- Nature Chemical Biology: Scientists develop new antibiotic against super bacteria 418
- Specialist: We have drop in hepatitis cases in Armenia, but rare cases of acute Hepatitis B and C are recorded 352
- New deadly disease reported in the world 346
- Find us on Facebook
- Poll