- Latest news▼
-
18:00, April 18 Daily Mail: Elderly woman in China gets infected with brain-eating amoeba
-
14:19, April 18 Obesity: exercising before breakfast helps you lose weight faster

-
10:42, April 18 The Conversation: childhood trauma can cause pathological hoarding

-
08:37, April 18 Daily Mail: Satiating food reduces cravings for sweets, nutritionist says

-
18:22, April 17 First Armenian-German Conference entitled “Heart Failure Spring School”

-
08:38, April 17 Why do kids usually recover from COVID-19 more easily than adults?

-
14:37, April 16 Daily Mail: intermittent fasting is not suitable for children and women before their periods

-
16:41, April 15 Cell: in carriers of defective BRCA2 gene, sugar consumption increases cancer risk

-
15:04, April 15 305 cases of measles recorded in Armenia so far in 2024
-
14:38, April 15 Food and Environmental Virology: tea contributes to effective coronavirus control

-
12:41, April 15 Daily Mail: vitamin A, B3 and E supplements can be dangerous
-
10:56, April 15 Diabetes Care: evening physical activity is good for the heart

-
08:27, April 15 Women are more susceptible to blood loss and death during bypass surgery than men, researchers say
-
18:42, April 13 WHO: Nigeria pioneers revolutionary meningitis vaccine
-
16:43, April 13 One-third of women experience menstruation-related migraines, most often during premenopause - study

All materials
Oral sex is to blame for dangerous ‘super gonorrhoea’ that could be incurable
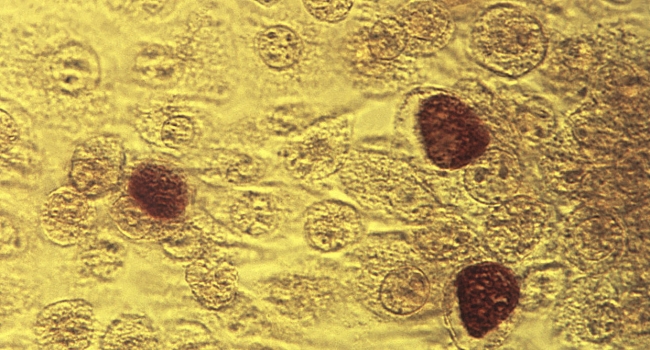
Oral sex is to blame for dangerous forms of untreatable gonorrhoea - and a lack of condom use is helping it spread, experts have warned.
Antibiotic resistant strains of the sexually transmitted infection (STI) are becoming much harder, and sometimes impossible, to treat, the World Health Organisation warns.
Dr Teodora Wi, medical officer in human reproduction at WHO, said: "The bacteria that cause gonorrhoea are particularly smart.
"Every time we use a new class of antibiotics to treat the infection, the bacteria evolve to resist them."
Figures from 77 countries shows the infection is becoming resistant to older and cheaper antibiotics.
And some countries, especially where incomes are high and STI tests are common, are finding cases that cannot be treated using all known antibiotics.
But worryingly, the vast majority of cases are in poorer countries where resistance is harder to detect.
Dr Wi added: "These cases may just be the tip of the iceberg, since systems to diagnose and report untreatable infections are lacking in lower-income countries where gonorrhoea is actually more common."
About 78 million people are infected with gonorrhoea each year, according to WHO.
It is the second most common form of STI in England.
It affects the genitals, rectum and throat, producing a thick green or yellow discharge from the vagina or penis.
Bacteria can be spread from the genitals through unprotected sex and from the throat through oral sex.
Dr Wi told the BBC: "When you use antibiotics to treat infections like a normal sore throat, this mixes with the Neisseria species [gonorrhoea bacteria] in your throat and this results in resistance."
Putting gonorrhoea bacteria into that environment through oral sex could lead to the spread of a super-gonorrhoea.
One in ten men and almost half of infected women will not experience any symptoms.
It can lead to pelvic inflammatory disease, ectopic pregnancy, infertility and an increased risk of HIV.
Between 2009 and 2014 97 per cent of countries under WHO's gonorrhoea surveillance programme found drug-resistant strains of the infection.
But there are just three new candidate drugs that could be used to curb the spread of the STI.
Follow NEWS.am Medicine on Facebook and Twitter
- Video
- Event calendar
- Archive
- Most read
month
week
day
- Pediatrics: Hypoglossal nerve stimulation implant helps with sleep apnea 1350
- Health minister: Simulation educational center will be created, assisted reproductive technology capacity will increase in Armenia 1307
- WHO: Nigeria pioneers revolutionary meningitis vaccine 1160
- One-third of women experience menstruation-related migraines, most often during premenopause - study 1128
- Women are more susceptible to blood loss and death during bypass surgery than men, researchers say 863
- Food and Environmental Virology: tea contributes to effective coronavirus control 847
- Daily Mail: vitamin A, B3 and E supplements can be dangerous 846
- Cell: in carriers of defective BRCA2 gene, sugar consumption increases cancer risk 815
- 305 cases of measles recorded in Armenia so far in 2024 809
- Diabetes Care: evening physical activity is good for the heart 799
- Daily Mail: intermittent fasting is not suitable for children and women before their periods 624
- First Armenian-German Conference entitled “Heart Failure Spring School” 413
- Why do kids usually recover from COVID-19 more easily than adults? 251
- The Conversation: childhood trauma can cause pathological hoarding 232
- Obesity: exercising before breakfast helps you lose weight faster 229
- Find us on Facebook
- Poll